| Uploader: | Abdulrashid |
| Date Added: | 07.02.2019 |
| File Size: | 9.55 Mb |
| Operating Systems: | Windows NT/2000/XP/2003/2003/7/8/10 MacOS 10/X |
| Downloads: | 32656 |
| Price: | Free* [*Free Regsitration Required] |
PPT – Standard Normal Distribution PowerPoint presentation | free to download - id: c5-ZGI5Y
Part 5: Normal Distribution | Free Worksheet and Solutions. In this article, we go through the definition of normal distribution, their key parameters, the z-score and empirical rule and provide examples, concept-check questions and solutions. So you know how to solve continuous random variables and functions, but you’re still unsure about Jul 26, · Suppose X has a normal distribution with mean 50 and standard deviation 6. About % of the x values lie between -1σ = (-1) (6) = -6 and 1σ = (1) (6) = 6 of the mean The values 50 - 6 = 44 and 50 + 6 = 56 are within 1 standard deviation of the mean The z-scores are -1 and +1 for 44 and 56, respectively A standard normal table (also called the unit normal table or z-score table) is a mathematical table for the values of ϕ, indicating the values of the cumulative distribution function of the normal distribution. Z-Score, also known as the standard score, indicates how many standard deviations an entity is, from the mean. Since probability tables cannot be printed for every normal distribution

Free download of standard normal distribution of z-scores
Subjects and resources that you bookmark will appear here. Light Mode. Browse Subjects. Cram Center. Join the Community. Study with Hours. Summer College Program. Sign in Join for Free. AP Stats. Unit 1. Harrison Burnside. Lusine Ghazaryan, free download of standard normal distribution of z-scores. Share Bookmark.
Free download of standard normal distribution of z-scores to Z-Scores This section free download of standard normal distribution of z-scores you to z-scores.
When I think of statistics, one of the first things that come in my mind is standard deviation and z-scores. So what are the z-scores? z-scores measure the distance of a value from the mean in standard deviations.
The formula is simple but very powerful. It is resistant to units, and it can be used to compare any activity. For this reason, z-scores are also called standardized values.
In sports, when the judges have to calculate the final score for athletes, use z- scores. The negative z- score means that the data value is below the meanwhile, the positive means that the data value is higher than the mean. The further the value is from the mean, irrespective of the sign, free download of standard normal distribution of z-scores, the unusual the value is.
Here is the formula for z-score:. As you see, when we are standardizing data into z-scores, we are shifting them by the mean and rescaling by the standard deviation.
But how does standardization affect the distribution? In general, shifting data changes the distribution but leaves the shape and spread unchanged. The center shifts with other measures of the position such as percentiles, min.
What about rescaling? AP exam MCQs always will ask questions like this to trick you if you know how the shifting and rescaling affect the shape, center, and spread. Get ready! You may have learned about Normal models or bell-shaped curves in your Algebra class and through calculus. Normal models are appropriate for symmetric and unimodal distributions.
The Normal model has two parameters: mean and standard deviation and written as N mean, sd. These parameters do not come from data but are part of the model. The Normal model with mean 0 and standard deviation 1 is called the Standard Normal model or the Standard Normal distribution. The Standard model can be written as N 0,1.
To standardize the Normal model, we need to subtract from mean and rescale by the standard deviation. Like with all the models we work, we have to make an assumption. In real-world data, hardly behaves normally, so our assumption is more realistic than idealistic. We check near Normal condition by looking at the histogram or Normal probability plot, free download of standard normal distribution of z-scores.
The histogram should look roughly symmetric and be unimodal. The Normal probability plot should look like a straight line. When we choose to make a histogram, we should check quantitative data condition, similar check Nearly Normal Condition, when you work with Normal models. Often we ask ourselves whether we are normal or not. If we are normal, then we should be doing about the same things as the average people do. The This rule works fine in Normal models, but do not ever try it for skewed distributions as it will fail.
The place where the bell shape starts to curve downward is called the inflection point, which is exactly one standard deviation away from the mean. Normal Curve. Standard Normal Distribution. Was this guide helpful? Sign up now for instant access to 2 amazing downloads to help you get a 5. Browse Study Guides By Unit. Intro to Z-Scores Normal Model Standard Normal Model The 68—95— Join us on Discord Thousands of students are studying with us for the AP Statistics exam.
Play this on HyperTyper Practice your typing skills while reading The Normal Distribution. Fiveable Who We Are Careers Help Center Terms of Use Privacy Policy CCPA Privacy Policy Leave Feedback.
Exam Question Types AP Psych FRQ APUSH LEQ AP Calc MCQ AP World DBQ AP Euro SAQ AP Gov FRQ AP Lang FRQ. Talk to a trained counselor for free. Text FIVEABLE to to get started.
Normal Distribution \u0026 Z-scores
, time: 10:20Free download of standard normal distribution of z-scores
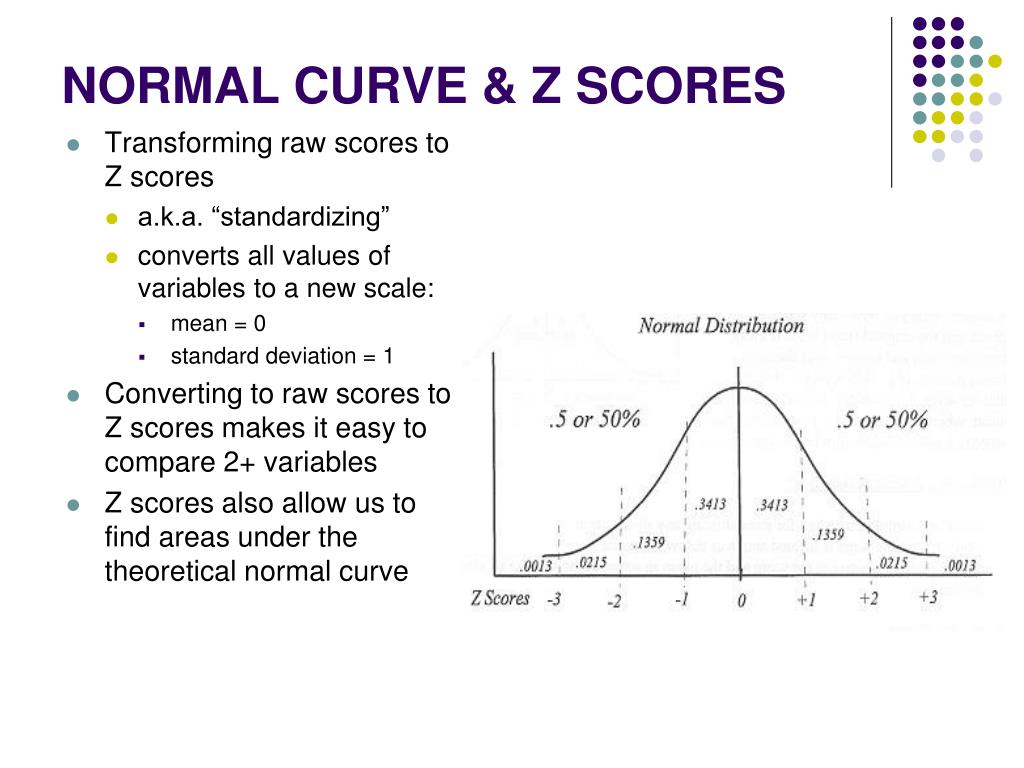
PPT – Standard Normal Distribution PowerPoint presentation | free to download - id: c5-ZGI5Y. The Adobe Flash plugin is needed to view this content. Get the plugin now. Actions. Standard Normal Distribution 6 Z-scores. A z-score measures the number of standard The standard deviation (SD) of the measurements. This defines the spread of your data in the normal distribution—or in plain English, how wide the curve should be. For instance, in the bell curve shown above, one standard deviation of the mean represents the range between exam scores of 53 and 85 Jul 26, · Suppose X has a normal distribution with mean 50 and standard deviation 6. About % of the x values lie between -1σ = (-1) (6) = -6 and 1σ = (1) (6) = 6 of the mean The values 50 - 6 = 44 and 50 + 6 = 56 are within 1 standard deviation of the mean The z-scores are -1 and +1 for 44 and 56, respectively

No comments:
Post a Comment